Ü D SPEC
·
D is the alphabetic code used
for Definition specifications.
To prompt D SPEC
give the line command: IPD
Prompt type . . . D Sequence number . . . '''''''
Declaration To /
Name E S/U Type From Length
_____________ _ _ __ _____ ______
Internal Decimal
Data Type Positions Keywords
_ __ _____________________________
Comment
________________
Ü D SPEC Keywords
o VARYING
D varstr s 50A VARYING
C eval varstr = 'Amit Jaiswal'
Here, the maximum
length of the variable varstr will be 50, but the
actual length can vary as per the value assigned to this variable. Here the
current size of variable will be the size of string “Amit Jaiswal”.
o *VARSIZE
*VARSIZE has nothing to do with the data type of the variable. All it
does is disable the compiler's validity checking of the length.
o EXPORT & IMPORT
Export indicates that the variable
has been defined (stored) in this module and will be used by some other module
which is importing this variable using Import
keyword.
Import indicates that the variable
has been defined (stored) in some other module and will be used here.
Example:
Columns . . . : 6 76 Edit AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> MODULE1
FMT H HKeywords++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
0001.00 HOPTION(*NODEBUGIO)
0002.00 DVAR1 S 5 0 EXPORT INZ(11111)
0003.00 DVAR2 S 5 0 IMPORT
0003.03 C CALLB 'MODULE2'
0003.04 C EVAL VAR1=VAR2 +33333 >>>>>>>>>>>>>>> VAR2=55555
0005.00 C VAR1 DSPLY
0006.00 C SETON LR
****************** End of data ****************************************
Columns . . . : 6 76 Edit AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> MODULE2
FMT D DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
0002.00 DVAR1 S 5 0 IMPORT
0003.00 DVAR3 S 5 0 IMPORT
0003.07 DVAR2 S 5 0 EXPORT
0003.08 C CALLB 'MODULE3'
0004.00 C EVAL VAR2=VAR1+VAR3 >>>>>>>>>>>>>>> VAR2=22222
0005.00 C RETURN
****************** End of data ****************************************
Columns . . . : 6 76 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> MODULE3
FMT D DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
0002.00 DVAR3 S 5 0 EXPORT
0004.00 C EVAL VAR3=11111 >>>>>>>>>> VAR3=11111
0004.01 C RETURN
****************** End of data ****************************************
CRTPGM PGM(AMIT/PGM1)
MODULE(AMIT/MODULE1 AMIT/MODULE2 AMIT/MODULE3)
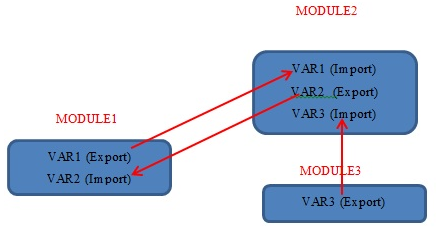
Below picture depicts
the data flow due to import/export:
o EXTPGM
This keyword is used in case of prototyping.
So first of all we will go through the concept of prototyping.
ü Prototyping
·
A
prototype tells the compiler how the parameters of a called program or
procedure are defined.
·
Prototyping
makes the compiler to verify that whatever parameters that will be passed to a
called program or procedure appropriately defined.
·
Prototyping
benefit us by showing the error at compile time rather than at run time.
ü Case1: Program without prototyping
Here, there is one rpgle program SENDPGM which calls a CL program ‘MSGSFLCL’ with parameters MSGID(7), MSGF(10) and MSGOPT(1).
Calling Program
SENDPGM
Columns . . . : 1 71 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> SENDPGM
FMT ** ...+... 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
* SEND MSG0001 FROM MESSAGE FILE CPF9898 TO PROGRAM MESSAGE QUEUE
C MOVEL 'MSG0001' MSGID
C MOVEL 'AM_MSGF' MSGF
C MOVE 'I' MSGOPT
C EXSR SEND
C SEND BEGSR
C CALL 'MSGSFLCL'
C PARM MSGID 7
C PARM MSGF 10
C PARM MSGOPT 1
C ENDSR
Message ID . . . . . . . . . : MSG0001
Message file . . . . . . . . : AM_MSGF
Library . . . . . . . . . : AMIT
Message text . . . . . . . . : THE ACCOUNT NUMBER CAN NOT BE BLANK
Called
program MSGSFLCL
Columns . . . : 1 71 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> MSGSFLCL
FMT ** ...+... 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
0001.01 PGM PARM(&MSGID &MSGF &MSGOPT)
0002.00 DCL VAR(&MSGID) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(7)
0003.00 DCL VAR(&MSGF) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(10)
0004.00 DCL VAR(&MSGOPT) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(1)
0006.00
0007.00
0008.00 IF COND(&MSGOPT *EQ 'I') THEN(SNDPGMMSG +
0009.00 MSGID(&MSGID) MSGF(&MSGF))
0010.00
0011.00 IF COND(&MSGOPT *EQ 'C') THEN(RMVMSG PGMQ(*PRV +
0012.00 (*)) CLEAR(*ALL))
0013.00 ENDPGM
****************** End of data ****************************************
When we run the program SENDPGM then at runtime it checks if the
parameters are appropriately passed or not. If we change PARM “MSGID” to some other data type or
change its length, we will get the error but not at compile time. We will get
the error at run time and our program cannot continue further.
To make sure that the program doesn’t crash at run time, we detect the error at compile time itself by using prototyping.
This is depicted in Case2 below.
ü Case2: Program with prototyping
To use prototyping, we do the following
modifications in the calling program SENDPFM.
Here we have changed the Parameter MSGID’s
length from 7 TO 3.
Columns . . . : 1 71 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> SENDPGM
FMT ** ...+... 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7
DMSGID S 3 >>>> Parm MSGID’s length changed from 7 to 3
DMSGF S 10
DMSGOPT S 1
DMSGSFLCL PR EXTPGM('MSGSFLCL')
DMSGID 7
DMSGF 10
DMSGOPT 1
* SEND MSG0001 FROM MESSAGE FILE CPF9898 TO PROGRAM MESSAGE QUEUE
C MOVEL 'MSG0001' MSGID
C MOVEL 'AM_MSGF' MSGF
C MOVE 'I' MSGOPT
C EXSR SEND
C SEND BEGSR
C CALLP MSGSFLCL(MSGID:MSGF:MSGOPT)
C ENDSR
Now when we compile
the program, we get the below error at compile
time.
**Error: The type and attributes of the parameter do not
match those of the prototype.
But the error that we have got here is at compile time
that is what we wanted.
o EXTPROC
If
you've built modules with commands like CRTRPGMOD, CRTCLMOD, CRTCBLMOD, and
CRTCMOD, you're accustomed to calling them with the CALLB op code. Just as you
can with CALL, you can replace CALLB with CALLP.
ü Case1: Program without prototyping
Calling Program
SENDPGM
Columns . . . : 1 71 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> SENDPGM
FMT ** ...+... 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
* SEND MSG0001 FROM MESSAGE FILE CPF9898 TO PROGRAM MESSAGE QUEUE
C MOVEL 'MSG0001' MSGID
C MOVEL 'AM_MSGF' MSGF
C MOVE 'I' MSGOPT
C EXSR SEND
C SEND BEGSR
C CALLB 'MSGSFLCL'
C PARM MSGID 7
C PARM MSGF 10
C PARM MSGOPT 1
C ENDSR
**Here we have
compiled the same CL using CRTCLMOD to make it a module.
Called module
MSGSFLCL
Columns . . . : 1 71 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> MSGSFLCL
FMT ** ...+... 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7
*************** Beginning of data *************************************
0001.01 PGM PARM(&MSGID &MSGF &MSGOPT)
0002.00 DCL VAR(&MSGID) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(7)
0003.00 DCL VAR(&MSGF) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(10)
0004.00 DCL VAR(&MSGOPT) TYPE(*CHAR) LEN(1)
0006.00
0007.00
0008.00 IF COND(&MSGOPT *EQ 'I') THEN(SNDPGMMSG +
0009.00 MSGID(&MSGID) MSGF(&MSGF))
0010.00
0011.00 IF COND(&MSGOPT *EQ 'C') THEN(RMVMSG PGMQ(*PRV +
0012.00 (*)) CLEAR(*ALL))
0013.00 ENDPGM
****************** End of data ****************************************
Now when we run the
program we get the same run time error. To avoid this we will go for
prototyping.
ü Case2: Program with prototyping
Columns . . . : 1 71 Browse AMIT/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> SENDPGM
FMT ** ...+... 1 ...+... 2 ...+... 3 ...+... 4 ...+... 5 ...+... 6 ...+... 7
DMSGID S 3 >>> Parm MSGID’s length changed from 7 to 3
DMSGF S 10
DMSGOPT S 1
DMSGSFLCL PR EXTPROC('MSGSFLCL')
DMSGID 7
DMSGF 10
DMSGOPT 1
* SEND MSG0001 FROM MESSAGE FILE CPF9898 TO PROGRAM MESSAGE QUEUE
C MOVEL 'MSG0001' MSGID
C MOVEL 'AM_MSGF' MSGF
C MOVE 'I' MSGOPT
C EXSR SEND
C SEND BEGSR
C CALLP MSGSFLCL(MSGID:MSGF:MSGOPT)
C ENDSR
Using this we get
the error at compile that we can correct and can easily avoid the situation of
any run time error due to parameters wrong definition.
o EXTNAME(file-name{:format-name}{:*ALL|
*INPUT|*OUTPUT|*KEY})
The EXTNAME keyword is used to specify the
name of the file which contains the field descriptions used as the subfield
description for the data structure being defined.
The file-name parameter is required.
Optionally a format name may be specified to direct the compiler to a specific format
within a file.
The last parameter specifies which fields in
the external record to extract:
·
*ALL extracts all fields.
·
*INPUT extracts just input capable fields.
·
*OUTPUT extracts just output capable fields.
·
*KEY extracts just key fields.
D Fileds1 E DS Export
D EXTNAME(file1)
Structure of the externally
described data structure:
·
Subfield name : Same as the external file’s fields name, unless it id renamed
by keyword EXTFLD
or the PREFIX keyword on a definition
specification is used to apply a prefix).
·
Subfield length
·
Subfield internal data type
All data structure
keywords except LIKEDS and LIKEREC are allowed with the EXTNAME keyword.
D D0220NEW E DS PREFIX(D21:3)
D EXTNAME(CZGD02H0:CZTD02H2)
D D0220OLD E DS PREFIX(D@@:3)
D EXTNAME(CZGD02H0:CZTD02H2)
o CONST(value)
* Constant variables
D INTRO C CONST('Introduction')
D PNDINT C CONST('Pending Introduction')
D PNDCHG C CONST('Pending Change')
The keyword
CONST(value) is used to identify the value of the constant.
o LIKE(RPG_name)
The
LIKE keyword allows us to define a data element of same data type and length as
another field. This keyword may be used
in place of the *LIKE DEFINE op-code.
* Variables
D SAVORGCOD S LIKE(D02ORGCOD) Inz
D SAVACNTNO S LIKE(D02ACNTNO) Inz
o
OVERLAY(name{:pos | *NEXT})
The
OVERLAY keyword allows us to define a field name on the basis of overlaying a data
structure or a data structure subfield.
D DataStruct DS
D MainField 10
D Field1 5 overlay(MainField)
D Field2 5 overlay(MainField:*next)
o OCCURS
* Below DS1 is
multiple occurrence data structures with 10 occurrences.
Columns . . . : 6 80 Browse AMITCC/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> MULTDS
FMT D DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data ****************************************************
0001.00 D DS1 DS OCCURS(10) >>>>
0002.00 D FLDA 1 5
0003.00 D FLDB 6 10
0004.00 DX S 2 0 INZ(1)
0005.00
0006.00 C X DO 10
0007.00 C X OCCUR DS1 >>> OCCUR op-code sets the occurrence to X
0008.00 C EVAL FLDA=%char(X)
0009.00 C EVAL FLDB=%char(X)
0010.00 C EVAL X=X+1
0011.00 C DS1 DSPLY
0012.00 C ENDDO
0013.00 C SETON LR
****************** End of data *******************************************************
OUTPUT
DSPLY 1
1
DSPLY 2
2
DSPLY 3
3
DSPLY 4
4
DSPLY 5
5
DSPLY 6
6
DSPLY 7
7
DSPLY 8
8
DSPLY 9
9
DSPLY 10
10
o
DTAARA{(data_area_name)}
Specifies the name
of the external data that is associated with a field, data structure, data structure subfield or data area data
structure.
Dtime_is S z
Dtime_isO S 20
DMATCHNF S 1 0 INZ (0)
DRBSPRTYM S 1 INZ ('N')
DACCCONVF S 1 INZ('N')
DLDA UDS DTAARA(*LDA)
DLdadateY 1 4 0
DLdadateM 5 6 0
DLdadateD 7 8 0
**Data structure for GETTING CURRENT DATE AND TIME
DCURTIMDAT DS
DCURTIMDATE 1 16S 0
DCURRYEAR 1 4S 0
DCURRMONTH 5 6S 0
DCURRDAY 7 8S 0
DCURRHRS 9 10S 0
DCURRMINS 11 12S 0
DCURRSECS 13 16S 0
C TIMECAL BEGSR
*
C EVAL TIME_IS=%TIMESTAMP()
C EVAL TIME_ISO=%char(TIME_IS:*iso0)
C EVAL CURRYEAR=%dec(%SUBST(TIMe_ISo:1:4):4:0)
C EVAL CURRMONTH=%dec(%SUBST(TIMe_ISo:5:2):2:0)
C EVAL CURRDAY=%dec(%SUBST(TIMe_ISo:7:2):2:0)
C EVAL CURRHRS=%dec(%SUBST(TIMe_ISo:9:2):2:0)
C EVAL CURRMINS=%dec(%SUBST(TIMe_ISo:11:2):2:0)
C EVAL CURRSECS=%dec(%SUBST(TIMe_ISo:13:4):4:0)
C ENDSR
OUTPUT
TIME_IS = '2012-05-18-07.11.00.926000'
TIME_ISO = '20120518071100926000'
o
CTDATA
Specifies that the array is a compile-time array.
Example is given after PERRCD definition.
o
DIM(numeric_constant)
Specifies the number of elements of an array
or table.
Example is given after PERRCD
definition.
o
PERRCD(numeric_constant)
Specifies
the number of elements per record for a compile-time or a prerun-time array or
table.
Example
Columns . . . : 1 100 Browse
SEU==>
FMT D .....DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data **************************************
0001.00 darr1 s 3P 0 dim(5) ctdata perrcd(1)
0002.00 darr2 s 3P 0 dim(5) ctdata perrcd(1)
0003.00 dS s 3p 0 inz(0)
0004.00 dn s 2p 0 inz(1)
0005.00 c n do 5
0006.00 c eval s=arr2(n)-arr1(n)
0007.00 c s dsply
0008.00 c add 1 n
0009.00 c enddo
0010.00 c seton lr
0011.00 ** CTDATA arr1
0012.00 101
0013.00 102
0014.00 103
0015.00 104
0016.00 105
0017.00 ** CTDATA arr2
0018.00 201
0019.00 202
0020.00 203
0021.00 204
0022.00 205
****************** End of data ********************************************
O/P
DSPLY 100
DSPLY 100
DSPLY 100
DSPLY 100
DSPLY 100
o
STATIC
Type this keyword
in the D specifications of sub-procedures to indicate that a standalone field or data structure is stored in static storage.
Automatic Storage
·
By default, whatever
stand-alone fields, data structures, arrays, etc. fields are defined inside a
sub-procedure use automatic storage.
·
The scope of these
sub-procedure’s fields will be till the sub-procedure runs. After that it will
be reset to default value(0 or blank).
·
It has no effect of SETON LR. It really doesn’t matter if LR is SETON
or SETOFF, its value will be reinitialized each time the procedure is called.
Static Storage
·
Static storage has its life
cycle from the time the program is called until the activation group where it
is running ends, or until the job or group job ends.
·
Static fields defined inside P
specs has no effect of SETON LR, its
values remain the same between multiple calls to the program.
·
Global variable is the one that
is defined outside P-spec. Its values remain the same between multiple calls to
the program. But it is affected by SETON
LR i.e. SETON LR resets the global variable.
Columns . . . : 1 80 Browse AMITCC/QRPGLESRC
SEU==> STATICPGM
FMT D .....DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data *****************************************************
0001.00 D Checkcount PR
0002.00 D n S 2 0 inz(1)
0003.00
0004.00 DDS1 DS
0005.00 DFiller1 12 inz(' Autocount=')
0006.00 DAuto 1 0
0007.00 DFiller2 14 inz(' Staticcount=')
0008.00 DStatic 1 0
0009.00 DFiller3 14 inz(' Globalcount=')
0010.00 DGlobalcount 1 0 inz(*zeros)
0011.00 C n DO 3
0012.00 C CALLP CHECKCOUNT
0013.00 C ENDDO
0014.00 C*** RETURN
0015.00 C SETON LR
0016.00
0017.00 P Checkcount B
0018.00 D PI
0019.00
0020.00 D AutoCount S 3 0
0021.00 D StaticCount S 3 0 STATIC
0022.00 C EVAL AutoCount=Autocount+1
0023.00 C EVAL StaticCount=StaticCount+1
0024.00 C EVAL Globalcount= Globalcount+1
0025.00
0026.00 C EVAL Auto=Autocount
0027.00 C EVAL Static=Staticcount
0028.00
0029.00 C DS1 DSPLY
0030.00
0031.00 P Checkcount E
0032.00
****************** End of data *********************************************************
Condition based OUTPUT :
Case1: 1ST CALL without RETURN op-code
Autocount=1 Staticcount=1
Globalcount=1
Autocount=1 Staticcount=2
Globalcount=2
Autocount=1
Staticcount=3 Globalcount=3
Case2: 2ND CALL without RETURN op-code
Autocount=1 Staticcount=4
Globalcount=1
Autocount=1 Staticcount=5
Globalcount=2
Autocount=1 Staticcount=6
Globalcount=3
Case3: 1ST CALL with RETURN op-code
Autocount=1 Staticcount=1
Globalcount=1
Autocount=1 Staticcount=2
Globalcount=2
Autocount=1 Staticcount=3
Globalcount=3
Case4: 2ND CALL with RETURN op-code
Autocount=1 Staticcount=4
Globalcount=4
Autocount=1 Staticcount=5
Globalcount=5
Autocount=1 Staticcount=6
Globalcount=6
Case5: 3RD
CALL with RETURN op-code after RCLRSC or SIGNOFF or RCLACTGRP (if used in the
program)
Autocount=1 Staticcount=1
Globalcount=1
Autocount=1 Staticcount=2
Globalcount=2
Autocount=1 Staticcount=3
Globalcount=3
o
INZ
Columns . . . : 6 100 Browse
SEU==>
FMT D DName+++++++++++ETDsFrom+++To/L+++IDc.Keywords+++++++++++++++++++++++
*************** Beginning of data ***********************************
0001.00 Da S 10A inz(*ALL'Z')
0002.00 Db S 10A inz(*blanks)
0003.00 Dc S 10 0 inz(*zeros)
0004.00 Dd S 10A inz
0005.00 De S 10 0 inz
0006.00 C a DSPLY
0007.00 C b DSPLY
0008.00 C c DSPLY
0009.00 C d DSPLY
0010.00 C e DSPLY
0011.00 C SETON LR
****************** End of data **************************************
O/P
DSPLY ZZZZZZZZZZ
DSPLY
DSPLY 0
DSPLY
DSPLY 0